Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences / HiLASE
General description
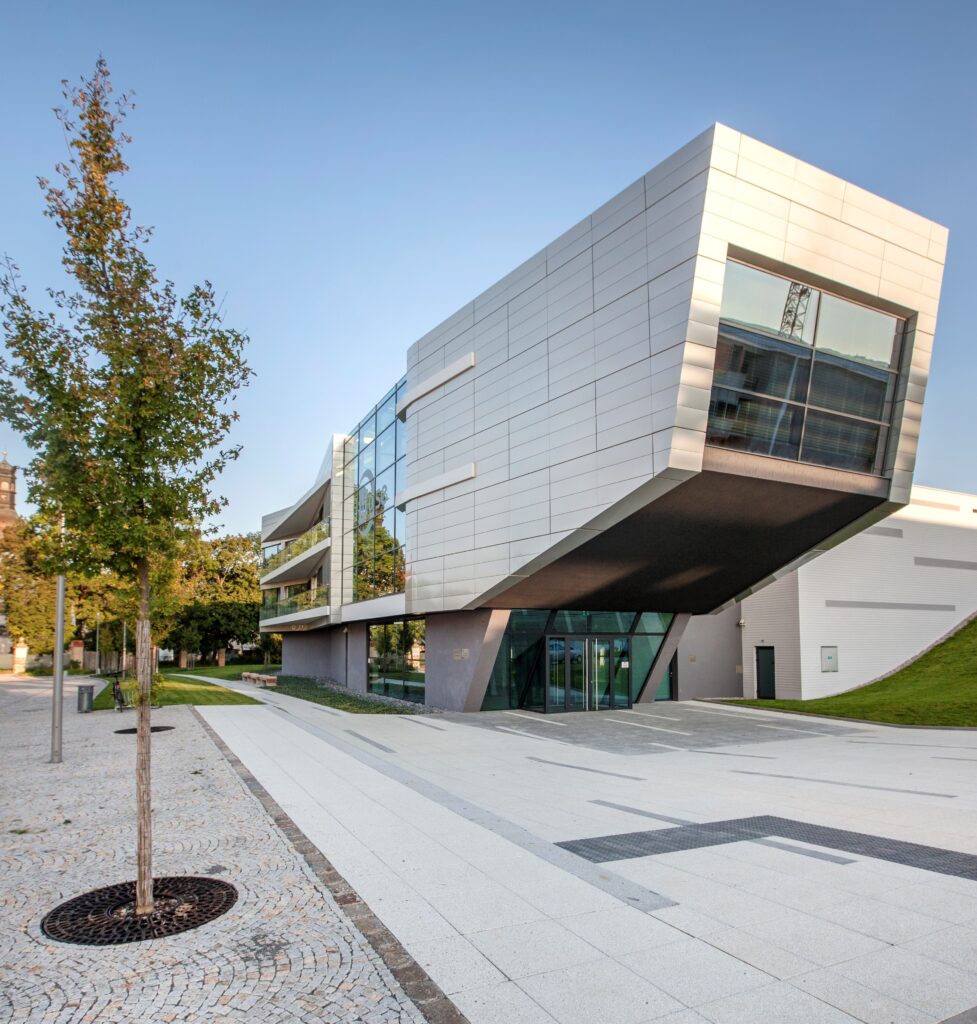
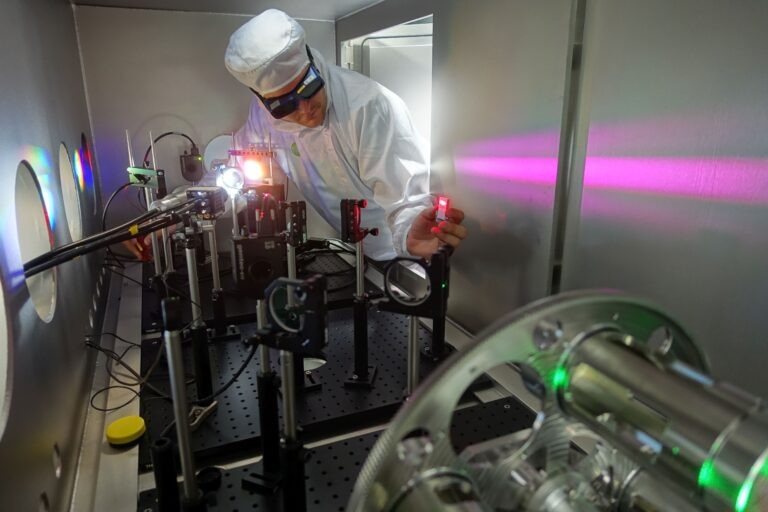
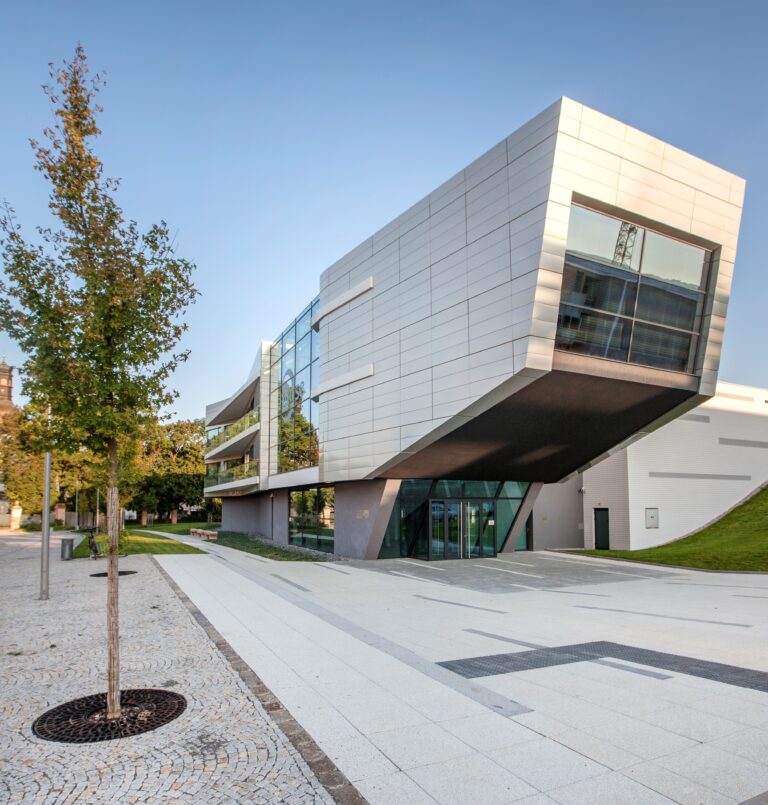
HiLASE is a laser research centre focusing on the experimental development of a new generation of lasers with high energy pulse or high frequency repetition that is more compact and stable than the devices currently available. It offers contract and cooperative research services as well as expert measurements and customization. The “next generation” laser technology is based on highly efficient diode pumped solid state laser (DPSSL) amplifiers. The multi-slab laser at HiLASE (“Bivoj”) represents the world’s first kW average power, high-energy, nanosecond pulsed diode pumped solid state laser. The HiLASE team also works on associated laser technologies, which include high-power optical isolators, adaptive optics, and characterization of laser materials at cryogenic temperatures. To testing durability and long-term stability of optical components, the Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) and Laser Shock Peening (LSP) station has been constructed. Both stations serve successfully for industrial companies, thus providing a roadmap to sustainability. HiLASE is a holder of the European HR Excellence in Research Award.
Key Research Facilities, Infrastructure and Equipment
- Laser system “BIVOJ”: kW-class nanosecond pulsed diode pumped solid state laser (DPSSL). First operation of the laser at the end of 2016 demonstrated amplification of 10 ns pulses at 10 Hz pulse repetition rate to the energy of 105 J at 1029.5 nm, representing the world’s first kW average power, high-energy, nanosecond pulsed DPSSL.
- Laser system “PERLA”: based upon Yb:Yag thin disk technology, offering ps and fs pulses at average powers up to 1 kW, over a range of energy and repetition rate combinations.
- Femtosecond micro-processing station: The microprocessing facility has been developed for irradiation of materials by ultrashort laser pulses (about 35 fs pulse duration) where the thermal effects, often undesirable, can be significantly reduced compared to the irradiation by longer laser pulse.
- Laser Induced Damage Threshold (LIDT) station: is defined as the highest quantity of laser radiation incident on an optical component for which the extrapolated probability of damage is zero. Optical components can be damaged by laser irradiation of sufficiently high energy or power.
- Laser shock peening (LSP) station: is a surface treatment process designed to improve mechanical properties and fatigue performance of various metals and alloys. The method utilizes a high intensity laser beam to generate strong pressure shock waves on the material surface.
Video reference from HiLASE
Contact person
Contact us to know more about our location and work environment. Please use the main contact for questions related to administrative matters. Please contact the supervisors/group leaders of respective research groups regarding feasibility of your research proposal with regard to the research group activities.

Your future supervisors

Jan Brajer

Jan Brajer
I am working on the development of laser production technologies. As a Head of department Industrial laser applications, I am trying to transfer scientific work, mostly with industrial partners, to the production, that means the ILA department is in touch with real problems. My biggest role is the leadership and the motivation of my colleagues to achieve established goals. I traveled the world to gather knowledge and help with the implementation of our solutions. I am working on national and international projects mostly focused on increasing the technical readiness level right now.
About the position
The Postdoctoral fellow will join the research team that is focused on laser applications and that is working to find solutions to different challenges in the field of advanced production. The key research infrastructure and equipment of this research group include pulsed lasers with high energy and the diagnostics for the surface properties evaluation.
The fellow has an opportunity to carry out secondments in the non-academic sector, in cooperation with our industrial partners, e.g SHM company, Eaton etc.
The postdoc position is focused on developing industrial relevant processes, which are not feasible with market existing laser sources yet. Our main objectives are to demonstrate the potential of a new generation of laser systems developed at HiLASE Centre in industrial applications and to initiate and influence further laser development according to industrial demands.
Besides science we are focused on the working culture, where it is possible to enforce our own ideas and to take responsibility for the part of researched areas.

Martin Smrž
martin.smrz@hilase.cz

martin.smrz@hilase.cz
Martin Smrž
From the very beginning of my professional career in 2004, I have focused on breakthrough ultrashort pulse solid state laser technology. Lately, as a researcher and Head of the Advanced laser development department at Hilase centre, I have energetically participated in the next development, customization, and transfer of these wonderful optical systems to high-tech industrial systems and applications. My personal interests are in development of the sub-kW class thin-disk pulsed laser systems in near- and mid-infrared spectral range with excellent beam quality, nonlinear frequency conversion to visible and UV spectral range, beam shaping, etc. I have long-term experience from scientific projects but also contractual research with industrial companies. I completed several international internships at institutes, such as, MIT Boston, USA, or CFEL in Hamburg, Germany.
About the position
The Postdoctoral fellow can join research teams of thin-disk femtosecond lasers, or nonlinear optics. Research activity of the teams is focused on development of pulsed solid state lasers, harmonic frequency conversion to visible an UV spectral range, or on mid-infrared optical parametric amplifiers. All the activities belong to state-of-the-art topics in the field of ultrashort pulses and laser technology, with many challenges and possibilities to publish original scientific results. However, the research is also application oriented and has direct scientific or industrial applications. We have been lately focusing also on laser technology for space applications. This is in DNA of the Hilase. Our research infrastructure can offer hi-tech equipment in a large ISO 7 clean room, software equipment, and support of a big and highly motivated research team.
The fellow may also cooperate with international collaborators in Europe, US, or Japan through international secondments or have the opportunity to carry out secondments in the non-academic sector, in cooperation with our industrial partners, e.g. famous crystal-growing and optical manufacturing company Crytur.
Given the main focus of our research group, the expected outputs of the fellowship can be both scientific publications, and applied research oriented results such as patent applications, prototypes coming from collaboration with industry, collaborative research projects, etc.
Potential applicants should have education in a field of physics, especially lasers and optics, however, other specialists able to bring new ideas and qualities well fitting our research group activities are welcomed – e.g. PhD in electrical or mechanical engineering with focus on fine mechanics, space technology, light detection and LIDARs, control systems and artificial intelligence for laser control, or manufacturing of optical components (bonding and gluing of optics, polishing, welding of glass, etc.).
The applicant should be ideally skilled in a laser lab and experimentally oriented, however, even specialists on physical and optical modeling, e.g. in Zemax, Solidworks, or Matlab would bring many new qualities to our research.